Why Is My Old Software Slow?
There are several reasons why your old software might be running slowly, and it’s up to developers to uncover the source. Like a mechanic inspecting each component of an old car to identify what’s causing issues, a developer must carefully examine the software from every angle, especially parts that have been patched or added over the years.
Source code, frameworks, infrastructure, or database: every element must be analyzed before a thorough diagnosis can be made.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common causes of software slowness.
1. Outdated Technology
Built with technologies that are no longer optimized or supported, legacy software is prone to performance issues. This is often the case with older versions of programming languages, which may lack key speed or security improvements.
Accessing deprecated libraries or dependencies can also severely impair performance.
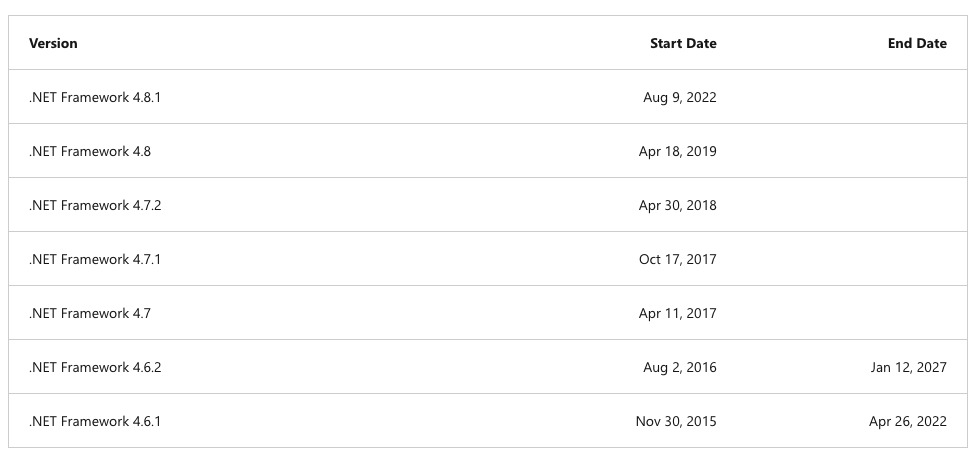
.NET Framework Obsolescence Table
2. Inadequate Software Architecture
Old monolithic architectures become harder to manage as they grow. When they become too bulky, they slow down. Their lack of modularity also makes maintenance and optimization more complex.
A monolithic system can also make it difficult to update or replace outdated components, often requiring a full overhaul to incorporate modern improvements.
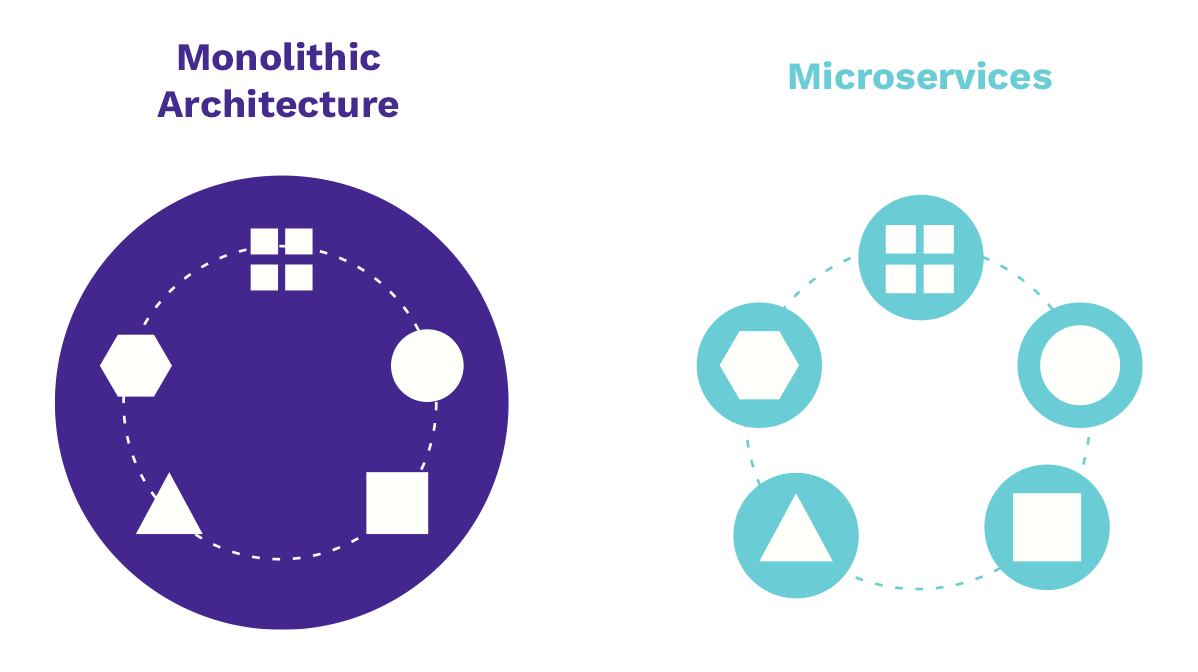
Monolithic Architecture vs. Microservices
3. Maintenance Issues
If your codebase has undergone decades of changes or quick fixes (like new feature additions), chances are it has become messy and hard to navigate, slowing things down.
Maintenance and updates can also be challenging if the code is poorly documented or inconsistently written.
4. Data Overload
Databases used by legacy systems can grow significantly over time, leading to slower query times and overall poor performance.
Older databases may also not be optimized for modern queries, which could require restructuring or migration to more efficient systems.
5. Lack of Optimization
Old software often lacks modern optimization techniques such as caching, SQL query tuning, or Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
Tasks might not be parallelized, and microservices may be absent, reducing the software’s speed and efficiency.
6. Increased Workload
As user bases grow beyond initial expectations, legacy systems may become overwhelmed and underperform.
Continually adding new features without optimizing the existing system can further strain performance, especially if the underlying infrastructure hasn’t been updated to handle the increased load.
7. External Dependencies
As mentioned earlier, outdated or poorly performing external modules or dependencies can drastically impact software performance. Network connectivity issues or access to unmaintained libraries can also play a role.
Solutions and Recommendations
Here are a few tips to improve legacy software performance:
Audit and Refactoring: Conduct a full code audit and refactor obsolete sections to improve software efficiency.
Technology Updates: Migrating to more recent technologies can significantly reduce bugs and improve performance.
Modern Architecture: Transitioning to a scalable and modern architecture (such as microservices) can enhance performance.
Database Optimization: Reorganize and optimize databases for faster query processing and better data management.
Use Modern Techniques: Consider modern optimization practices like caching, SQL query tuning, or CDNs for static resources.
Continuous Learning: Encourage ongoing training in best practices and modern tools to support high-performing software.
Conclusion
Outdated technologies, poor architecture, data overload, rising user loads, lack of optimization, and maintenance issues are all valid explanations for a slow software system.
Sluggish performance can be highly detrimental to the success of a custom application. For example, according to The App Attention Span Study by AppDynamics and the Institute of Management Studies (IMS) at Goldsmiths, University of London, nearly 90% of users have stopped using an app due to poor performance.
Investing in a redesign or modernization effort can boost productivity, strengthen your competitive edge, and increase user engagement.







